Paper YOLO v4: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934
Paper Scaled YOLO v4: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.08036 use to reproduce results: ScaledYOLOv4
More details in articles on medium: * Scaled_YOLOv4 * YOLOv4
Manual: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/wiki
Discussion: - Reddit - Google-groups - Discord
About Darknet framework: http://pjreddie.com/darknet/
Yolo v4 in other frameworks (TensorRT, TensorFlow, PyTorch, OpenVINO, OpenCV-dnn, TVM,...)
How to compile on Linux
How to compile on Windows
How to mark bounded boxes of objects and create annotation files

 AP50:95 - FPS (Tesla V100) Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.08036
AP50:95 - FPS (Tesla V100) Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.08036
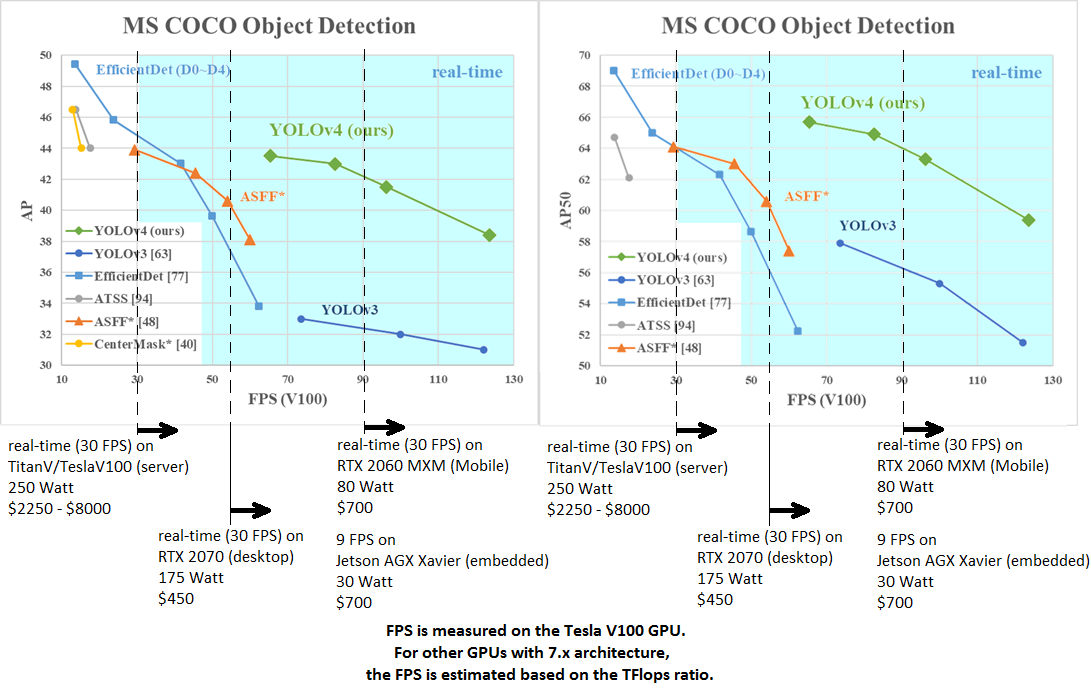 AP50:95 / AP50 - FPS (Tesla V100) Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934
AP50:95 / AP50 - FPS (Tesla V100) Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934
tkDNN-TensorRT accelerates YOLOv4 ~2x times for batch=1 and 3x-4x times for batch=4. * tkDNN: https://github.com/ceccocats/tkDNN * OpenCV: https://gist.github.com/YashasSamaga/48bdb167303e10f4d07b754888ddbdcf
| Network Size | Darknet, FPS (avg) | tkDNN TensorRT FP32, FPS | tkDNN TensorRT FP16, FPS | OpenCV FP16, FPS | tkDNN TensorRT FP16 batch=4, FPS | OpenCV FP16 batch=4, FPS | tkDNN Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | 100 | 116 | 202 | 183 | 423 | 430 | 4.3x |
| 416 | 82 | 103 | 162 | 159 | 284 | 294 | 3.6x |
| 512 | 69 | 91 | 134 | 138 | 206 | 216 | 3.1x |
| 608 | 53 | 62 | 103 | 115 | 150 | 150 | 2.8x |
| Tiny 416 | 443 | 609 | 790 | 773 | 1774 | 1353 | 3.5x |
| Tiny 416 CPU Core i7 7700HQ | 3.4 | - | - | 42 | - | 39 | 12x |
Yolo v4 Full comparison: map_fps
Yolo v4 tiny comparison: tiny_fps
CSPNet: paper and map_fps comparison: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
Yolo v3 on MS COCO: Speed / Accuracy (mAP@0.5) chart
Yolo v3 on MS COCO (Yolo v3 vs RetinaNet) - Figure 3: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767v1.pdf
Yolo v2 on Pascal VOC 2007: https://hsto.org/files/a24/21e/068/a2421e0689fb43f08584de9d44c2215f.jpg
Yolo v2 on Pascal VOC 2012 (comp4): https://hsto.org/files/3a6/fdf/b53/3a6fdfb533f34cee9b52bdd9bb0b19d9.jpg
 |  |
|---|---|
Others: https://www.youtube.com/user/pjreddie/videos
Download and unzip test-dev2017 dataset from MS COCO server: http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/test2017.zip
Download list of images for Detection taks and replace the paths with yours: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/scripts/testdev2017.txt
Download yolov4.weights file 245 MB: yolov4.weights (Google-drive mirror yolov4.weights )
Content of the file cfg/coco.data should be
classes= 80 train = <replace with your path>/trainvalno5k.txt valid = <replace with your path>/testdev2017.txt names = data/coco.names backup = backup eval=coco
Create /results/ folder near with ./darknet executable file
Run validation: ./darknet detector valid cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights
Rename the file /results/coco_results.json to detections_test-dev2017_yolov4_results.json and compress it to detections_test-dev2017_yolov4_results.zip
Submit file detections_test-dev2017_yolov4_results.zip to the MS COCO evaluation server for the test-dev2019 (bbox)
Compile Darknet with GPU=1 CUDNN=1 CUDNN_HALF=1 OPENCV=1 in the Makefile
Download yolov4.weights file 245 MB: yolov4.weights (Google-drive mirror yolov4.weights )
Get any .avi/.mp4 video file (preferably not more than 1920x1080 to avoid bottlenecks in CPU performance)
Run one of two commands and look at the AVG FPS:
include video_capturing + NMS + drawing_bboxes: ./darknet detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4 -dont_show -ext_output
exclude video_capturing + NMS + drawing_bboxes: ./darknet detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4 -benchmark
There are weights-file for different cfg-files (trained for MS COCO dataset):
FPS on RTX 2070 (R) and Tesla V100 (V):
yolov4x-mish.cfg - 640x640 - 67.9% mAP@0.5 (49.4% AP@0.5:0.95) - 23(R) FPS / 50(V) FPS - 221 BFlops (110 FMA) - 381 MB: yolov4x-mish.weights
pre-trained weights for training: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v4_pre/yolov4x-mish.conv.166
yolov4-csp.cfg - 202 MB: yolov4-csp.weights paper Scaled Yolo v4
just change width= and height= parameters in yolov4-csp.cfg file and use the same yolov4-csp.weights file for all cases:
* width=640 height=640 in cfg: 66.2% mAP@0.5 (47.5% AP@0.5:0.95) - 70(V) FPS - 120 (60 FMA) BFlops
* width=512 height=512 in cfg: 64.8% mAP@0.5 (46.2% AP@0.5:0.95) - 93(V) FPS - 77 (39 FMA) BFlops
* pre-trained weights for training: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v4_pre/yolov4-csp.conv.142
yolov4.cfg - 245 MB: yolov4.weights (Google-drive mirror yolov4.weights ) paper Yolo v4just change width= and height= parameters in yolov4.cfg file and use the same yolov4.weights file for all cases:
width=608 height=608 in cfg: 65.7% mAP@0.5 (43.5% AP@0.5:0.95) - 34(R) FPS / 62(V) FPS - 128.5 BFlops
width=512 height=512 in cfg: 64.9% mAP@0.5 (43.0% AP@0.5:0.95) - 45(R) FPS / 83(V) FPS - 91.1 BFlops
width=416 height=416 in cfg: 62.8% mAP@0.5 (41.2% AP@0.5:0.95) - 55(R) FPS / 96(V) FPS - 60.1 BFlops
width=320 height=320 in cfg: 60% mAP@0.5 ( 38% AP@0.5:0.95) - 63(R) FPS / 123(V) FPS - 35.5 BFlops
yolov4-tiny.cfg - 40.2% mAP@0.5 - 371(1080Ti) FPS / 330(RTX2070) FPS - 6.9 BFlops - 23.1 MB: yolov4-tiny.weights
enet-coco.cfg (EfficientNetB0-Yolov3) - 45.5% mAP@0.5 - 55(R) FPS - 3.7 BFlops - 18.3 MB: enetb0-coco_final.weights
yolov3-openimages.cfg - 247 MB - 18(R) FPS - OpenImages dataset: yolov3-openimages.weights
Put it near compiled: darknet.exe
You can get cfg-files by path: darknet/cfg/
Windows or Linux
CMake >= 3.12: https://cmake.org/download/
CUDA >= 10.0: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive (on Linux do Post-installation Actions)
OpenCV >= 2.4: use your preferred package manager (brew, apt), build from source using vcpkg or download from OpenCV official site (on Windows set system variable OpenCV_DIR = C:\opencv\build - where are the include and x64 folders image)
cuDNN >= 7.0 https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive (on Linux copy cudnn.h,libcudnn.so... as desribed here https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/sdk/cudnn-install/index.html#installlinux-tar , on Windows copy cudnn.h,cudnn64_7.dll, cudnn64_7.lib as desribed here https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/sdk/cudnn-install/index.html#installwindows )
GPU with CC >= 3.0: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CUDA#GPUs_supported
on Linux GCC or Clang, on Windows MSVC 2017/2019 https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/thank-you-downloading-visual-studio/?sku=Community
Pytorch - Scaled-YOLOv4: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/ScaledYOLOv4
TensorFlow: pip install yolov4 YOLOv4 on TensorFlow 2.0 / TFlite / Andriod: https://github.com/hunglc007/tensorflow-yolov4-tflite
Official TF models: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/vision/beta/projects/yolo
For YOLOv4 - convert yolov4.weights/cfg files to yolov4.pb by using TNTWEN project, and to yolov4.tflite TensorFlow-lite
OpenCV-dnn the fastest implementation of YOLOv4 for CPU (x86/ARM-Android), OpenCV can be compiled with OpenVINO-backend for running on (Myriad X / USB Neural Compute Stick / Arria FPGA), use yolov4.weights/cfg with: C++ example or Python example
Intel OpenVINO 2021.2: supports YOLOv4 (NPU Myriad X / USB Neural Compute Stick / Arria FPGA): https://devmesh.intel.com/projects/openvino-yolov4-49c756 read this manual (old manual )
Tencent/ncnn: the fastest inference of YOLOv4 on mobile phone CPU: https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn
PyTorch > ONNX:
ONNX on Jetson for YOLOv4: https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/announcing-onnx-runtime-for-jetson/
TensorRT YOLOv4 on TensorRT+tkDNN: https://github.com/ceccocats/tkDNN For YOLOv3 (-70% faster inference): Yolo is natively supported in DeepStream 4.0 read PDF. jkjung-avt/tensorrt_demos or wang-xinyu/tensorrtx implemented yolov3-spp, yolov4, etc.
Deepstream 5.0 / TensorRT for YOLOv4 https://github.com/NVIDIA-AI-IOT/yolov4_deepstream or https://github.com/marcoslucianops/DeepStream-Yolo
Triton Inference Server / TensorRT https://github.com/isarsoft/yolov4-triton-tensorrt
Xilinx Zynq Ultrascale+ Deep Learning Processor (DPU) ZCU102/ZCU104: https://github.com/Xilinx/Vitis-In-Depth-Tutorial/tree/master/Machine_Learning/Design_Tutorials/07-yolov4-tutorial
Amazon Neurochip / Amazon EC2 Inf1 instances 1.85 times higher throughput and 37% lower cost per image for TensorFlow based YOLOv4 model, using Keras URL
TVM - compilation of deep learning models (Keras, MXNet, PyTorch, Tensorflow, CoreML, DarkNet) into minimum deployable modules on diverse hardware backends (CPUs, GPUs, FPGA, and specialized accelerators): https://tvm.ai/about
OpenDataCam - It detects, tracks and counts moving objects by using YOLOv4: https://github.com/opendatacam/opendatacam#-hardware-pre-requisite
Netron - Visualizer for neural networks: https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron
MS COCO: use ./scripts/get_coco_dataset.sh to get labeled MS COCO detection dataset
OpenImages: use python ./scripts/get_openimages_dataset.py for labeling train detection dataset
Pascal VOC: use python ./scripts/voc_label.py for labeling Train/Test/Val detection datasets
ILSVRC2012 (ImageNet classification): use ./scripts/get_imagenet_train.sh (also imagenet_label.sh for labeling valid set)
German/Belgium/Russian/LISA/MASTIF Traffic Sign Datasets for Detection - use this parsers: https://github.com/angeligareta/Datasets2Darknet#detection-task
List of other datasets: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/tree/master/scripts#datasets
developed State-of-the-Art object detector YOLOv4
added State-of-Art models: CSP, PRN, EfficientNet
added layers: [conv_lstm], [scale_channels] SE/ASFF/BiFPN, [local_avgpool], [sam], [Gaussian_yolo], [reorg3d] (fixed [reorg]), fixed [batchnorm]
added the ability for training recurrent models (with layers conv-lstm[conv_lstm]/conv-rnn[crnn]) for accurate detection on video
added data augmentation: [net] mixup=1 cutmix=1 mosaic=1 blur=1. Added activations: SWISH, MISH, NORM_CHAN, NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX
added the ability for training with GPU-processing using CPU-RAM to increase the mini_batch_size and increase accuracy (instead of batch-norm sync)
improved binary neural network performance 2x-4x times for Detection on CPU and GPU if you trained your own weights by using this XNOR-net model (bit-1 inference) : https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/cfg/yolov3-tiny_xnor.cfg
improved neural network performance ~7% by fusing 2 layers into 1: Convolutional + Batch-norm
improved performance: Detection 2x times, on GPU Volta/Turing (Tesla V100, GeForce RTX, ...) using Tensor Cores if CUDNN_HALF defined in the Makefile or darknet.sln
improved performance ~1.2x times on FullHD, ~2x times on 4K, for detection on the video (file/stream) using darknet detector demo...
improved performance 3.5 X times of data augmentation for training (using OpenCV SSE/AVX functions instead of hand-written functions) - removes bottleneck for training on multi-GPU or GPU Volta
improved performance of detection and training on Intel CPU with AVX (Yolo v3 ~85%)
optimized memory allocation during network resizing when random=1
optimized GPU initialization for detection - we use batch=1 initially instead of re-init with batch=1
added correct calculation of mAP, F1, IoU, Precision-Recall using command darknet detector map...
added drawing of chart of average-Loss and accuracy-mAP (-map flag) during training
run ./darknet detector demo ... -json_port 8070 -mjpeg_port 8090 as JSON and MJPEG server to get results online over the network by using your soft or Web-browser
added calculation of anchors for training
added example of Detection and Tracking objects: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp
run-time tips and warnings if you use incorrect cfg-file or dataset
added support for Windows
many other fixes of code...
And added manual - How to train Yolo v4-v2 (to detect your custom objects)
Also, you might be interested in using a simplified repository where is implemented INT8-quantization (+30% speedup and -1% mAP reduced): https://github.com/AlexeyAB/yolo2_light
On Linux use ./darknet instead of darknet.exe, like this:./darknet detector test ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov4.cfg ./yolov4.weights
On Linux find executable file ./darknet in the root directory, while on Windows find it in the directory \build\darknet\x64
Yolo v4 COCO - image: darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -thresh 0.25
Output coordinates of objects: darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output dog.jpg
Yolo v4 COCO - video: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output test.mp4
Yolo v4 COCO - WebCam 0: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -c 0
Yolo v4 COCO for net-videocam - Smart WebCam: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights http://192.168.0.80:8080/video?dummy=param.mjpg
Yolo v4 - save result videofile res.avi: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4 -out_filename res.avi
Yolo v3 Tiny COCO - video: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.weights test.mp4
JSON and MJPEG server that allows multiple connections from your soft or Web-browser ip-address:8070 and 8090: ./darknet detector demo ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov3.cfg ./yolov3.weights test50.mp4 -json_port 8070 -mjpeg_port 8090 -ext_output
Yolo v3 Tiny on GPU #1: darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.weights -i 1 test.mp4
Alternative method Yolo v3 COCO - image: darknet.exe detect cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -i 0 -thresh 0.25
Train on Amazon EC2, to see mAP & Loss-chart using URL like: http://ec2-35-160-228-91.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com:8090 in the Chrome/Firefox (Darknet should be compiled with OpenCV): ./darknet detector train cfg/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show -mjpeg_port 8090 -map
186 MB Yolo9000 - image: darknet.exe detector test cfg/combine9k.data cfg/yolo9000.cfg yolo9000.weights
Remeber to put data/9k.tree and data/coco9k.map under the same folder of your app if you use the cpp api to build an app
To process a list of images data/train.txt and save results of detection to result.json file use: darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output -dont_show -out result.json < data/train.txt
To process a list of images data/train.txt and save results of detection to result.txt use: darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -dont_show -ext_output < data/train.txt > result.txt
Pseudo-lableing - to process a list of images data/new_train.txt and save results of detection in Yolo training format for each image as label <image_name>.txt (in this way you can increase the amount of training data) use:darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -thresh 0.25 -dont_show -save_labels < data/new_train.txt
To calculate anchors: darknet.exe detector calc_anchors data/obj.data -num_of_clusters 9 -width 416 -height 416
To check accuracy mAP@IoU=50: darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights
To check accuracy mAP@IoU=75: darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights -iou_thresh 0.75
Download for Android phone mjpeg-stream soft: IP Webcam / Smart WebCam
Smart WebCam - preferably: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.acontech.android.SmartWebCam2
IP Webcam: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.pas.webcam
Connect your Android phone to computer by WiFi (through a WiFi-router) or USB
Start Smart WebCam on your phone
Replace the address below, on shown in the phone application (Smart WebCam) and launch:
Yolo v4 COCO-model: darknet.exe detector demo data/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights http://192.168.0.80:8080/video?dummy=param.mjpg -i 0
CMake)The CMakeLists.txt will attempt to find installed optional dependencies like CUDA, cudnn, ZED and build against those. It will also create a shared object library file to use darknet for code development.
Open a shell terminal inside the cloned repository and launch:
./build.sh
make)Just do make in the darknet directory. (You can try to compile and run it on Google Colab in cloud link (press «Open in Playground» button at the top-left corner) and watch the video link )
Before make, you can set such options in the Makefile: link
GPU=1 to build with CUDA to accelerate by using GPU (CUDA should be in /usr/local/cuda)
CUDNN=1 to build with cuDNN v5-v7 to accelerate training by using GPU (cuDNN should be in /usr/local/cudnn)
CUDNN_HALF=1 to build for Tensor Cores (on Titan V / Tesla V100 / DGX-2 and later) speedup Detection 3x, Training 2x
OPENCV=1 to build with OpenCV 4.x/3.x/2.4.x - allows to detect on video files and video streams from network cameras or web-cams
DEBUG=1 to bould debug version of Yolo
OPENMP=1 to build with OpenMP support to accelerate Yolo by using multi-core CPU
LIBSO=1 to build a library darknet.so and binary runable file uselib that uses this library. Or you can try to run so LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib test.mp4 How to use this SO-library from your own code - you can look at C++ example: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp
or use in such a way: LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib data/coco.names cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4
ZED_CAMERA=1 to build a library with ZED-3D-camera support (should be ZED SDK installed), then runLD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib data/coco.names cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights zed_camera
You also need to specify for which graphics card the code is generated. This is done by setting ARCH=. If you use a never version than CUDA 11 you further need to edit line 20 from Makefile and remove -gencode arch=compute_30,code=sm_30 \ as Kepler GPU support was dropped in CUDA 11. You can also drop the general ARCH= and just uncomment ARCH= for your graphics card.
To run Darknet on Linux use examples from this article, just use ./darknet instead of darknet.exe, i.e. use this command: ./darknet detector test ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov4.cfg ./yolov4.weights
CMake)Requires:
* MSVS: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/thank-you-downloading-visual-studio/?sku=Community
* Cmake GUI: Windows win64-x64 Installerhttps://cmake.org/download/
* Download Darknet zip-archive with the latest commit and uncompress it: master.zip
In the Windows:
Start (button) -> All programms -> Cmake -> Cmake (gui) ->
look at image In Cmake: Enter input path to the darknet Source, and output path to the Binaries -> Configure (button) -> Optional platform for generator: x64 -> Finish -> Generate -> Open Project ->
in MS Visual Studio: Select: x64 and Release -> Build -> Build solution
find the executable file darknet.exe in the output path to the binaries you specified
vcpkg)This is the recommended approach to build Darknet on Windows.
Install Visual Studio 2017 or 2019. In case you need to download it, please go here: Visual Studio Community
Install CUDA (at least v10.0) enabling VS Integration during installation.
Open Powershell (Start -> All programs -> Windows Powershell) and type these commands:
PS Code\> git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg PS Code\> cd vcpkg PS Code\vcpkg> $env:VCPKG_ROOT=$PWD PS Code\vcpkg> .\bootstrap-vcpkg.bat PS Code\vcpkg> .\vcpkg install darknet[full]:x64-windows #replace with darknet[opencv-base,cuda,cudnn]:x64-windows for a quicker install of dependencies PS Code\vcpkg> cd .. PS Code\> git clone https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet PS Code\> cd darknet PS Code\darknet> powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\build.ps1
Train it first on 1 GPU for like 1000 iterations: darknet.exe detector train cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.conv.137
Then stop and by using partially-trained model /backup/yolov4_1000.weights run training with multigpu (up to 4 GPUs): darknet.exe detector train cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg /backup/yolov4_1000.weights -gpus 0,1,2,3
If you get a Nan, then for some datasets better to decrease learning rate, for 4 GPUs set learning_rate = 0,00065 (i.e. learning_rate = 0.00261 / GPUs). In this case also increase 4x times burn_in = in your cfg-file. I.e. use burn_in = 4000 instead of 1000.
https://groups.google.com/d/msg/darknet/NbJqonJBTSY/Te5PfIpuCAAJ
(to train old Yolo v2 yolov2-voc.cfg, yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg, yolo-voc.cfg, yolo-voc.2.0.cfg, ... click by the link)
Training Yolo v4 (and v3):
For training cfg/yolov4-custom.cfg download the pre-trained weights-file (162 MB): yolov4.conv.137 (Google drive mirror yolov4.conv.137 )
Create file yolo-obj.cfg with the same content as in yolov4-custom.cfg (or copy yolov4-custom.cfg to yolo-obj.cfg) and:
change line batch to batch=64
change line subdivisions to subdivisions=16
change line max_batches to (classes*2000 but not less than number of training images, but not less than number of training images and not less than 6000), f.e. max_batches=6000 if you train for 3 classes
change line steps to 80% and 90% of max_batches, f.e. steps=4800,5400
set network size width=416 height=416 or any value multiple of 32: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L8-L9
change line classes=80 to your number of objects in each of 3 [yolo]-layers:
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L610
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L696
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L783
change [filters=255] to filters=(classes + 5)x3 in the 3 [convolutional] before each [yolo] layer, keep in mind that it only has to be the last [convolutional] before each of the [yolo] layers.
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L603
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L689
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L776
when using [Gaussian_yolo] layers, change [filters=57] filters=(classes + 9)x3 in the 3 [convolutional] before each [Gaussian_yolo] layer
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L604
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L696
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L789
So if classes=1 then should be filters=18. If classes=2 then write filters=21.
(Do not write in the cfg-file: filters=(classes + 5)x3)
(Generally filters depends on the classes, coords and number of masks, i.e. filters=(classes + coords + 1)*<number of mask>, where mask is indices of anchors. If mask is absence, then filters=(classes + coords + 1)*num)
So for example, for 2 objects, your file yolo-obj.cfg should differ from yolov4-custom.cfg in such lines in each of 3 [yolo]-layers:
[convolutional] filters=21 [region] classes=2
Create file obj.names in the directory build\darknet\x64\data\, with objects names - each in new line
Create file obj.data in the directory build\darknet\x64\data\, containing (where classes = number of objects):
ini
classes = 2
train = data/train.txt
valid = data/test.txt
names = data/obj.names
backup = backup/
Put image-files (.jpg) of your objects in the directory build\darknet\x64\data\obj\
You should label each object on images from your dataset. Use this visual GUI-software for marking bounded boxes of objects and generating annotation files for Yolo v2 & v3: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
It will create .txt-file for each .jpg-image-file - in the same directory and with the same name, but with .txt-extension, and put to file: object number and object coordinates on this image, for each object in new line:
<object-class> <x_center> <y_center> <width> <height>
Where:
* <object-class> - integer object number from 0 to (classes-1)
* <x_center> <y_center> <width> <height> - float values relative to width and height of image, it can be equal from (0.0 to 1.0]
* for example: <x> = <absolute_x> / <image_width> or <height> = <absolute_height> / <image_height>
* atention: <x_center> <y_center> - are center of rectangle (are not top-left corner)
For example for img1.jpg you will be created img1.txt containing:
1 0.716797 0.395833 0.216406 0.147222
0 0.687109 0.379167 0.255469 0.158333
1 0.420312 0.395833 0.140625 0.166667
Create file train.txt in directory build\darknet\x64\data\, with filenames of your images, each filename in new line, with path relative to darknet.exe, for example containing:
data/obj/img1.jpg
data/obj/img2.jpg
data/obj/img3.jpg
Download pre-trained weights for the convolutional layers and put to the directory build\darknet\x64
for yolov4.cfg, yolov4-custom.cfg (162 MB): yolov4.conv.137 (Google drive mirror yolov4.conv.137 )
for yolov4-tiny.cfg, yolov4-tiny-3l.cfg, yolov4-tiny-custom.cfg (19 MB): yolov4-tiny.conv.29
for csresnext50-panet-spp.cfg (133 MB): csresnext50-panet-spp.conv.112
for yolov3.cfg, yolov3-spp.cfg (154 MB): darknet53.conv.74
for yolov3-tiny-prn.cfg , yolov3-tiny.cfg (6 MB): yolov3-tiny.conv.11
for enet-coco.cfg (EfficientNetB0-Yolov3) (14 MB): enetb0-coco.conv.132
Start training by using the command line: darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137
To train on Linux use command: ./darknet detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 (just use ./darknet instead of darknet.exe)
(file yolo-obj_last.weights will be saved to the build\darknet\x64\backup\ for each 100 iterations)
(file yolo-obj_xxxx.weights will be saved to the build\darknet\x64\backup\ for each 1000 iterations)
(to disable Loss-Window use darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show, if you train on computer without monitor like a cloud Amazon EC2)
(to see the mAP & Loss-chart during training on remote server without GUI, use command darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show -mjpeg_port 8090 -map then open URL http://ip-address:8090 in Chrome/Firefox browser)
8.1. For training with mAP (mean average precisions) calculation for each 4 Epochs (set valid=valid.txt or train.txt in obj.data file) and run: darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -map
After training is complete - get result yolo-obj_final.weights from path build\darknet\x64\backup\
After each 100 iterations you can stop and later start training from this point. For example, after 2000 iterations you can stop training, and later just start training using: darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_2000.weights
(in the original repository https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet the weights-file is saved only once every 10 000 iterations if(iterations > 1000))
Also you can get result earlier than all 45000 iterations.
Note: If during training you see nan values for avg (loss) field - then training goes wrong, but if nan is in some other lines - then training goes well.
Note: If you changed width= or height= in your cfg-file, then new width and height must be divisible by 32.
Note: After training use such command for detection: darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights
Note: if error Out of memory occurs then in .cfg-file you should increase subdivisions=16, 32 or 64: link
Do all the same steps as for the full yolo model as described above. With the exception of:
* Download file with the first 29-convolutional layers of yolov4-tiny: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v4_pre/yolov4-tiny.conv.29
(Or get this file from yolov4-tiny.weights file by using command: darknet.exe partial cfg/yolov4-tiny-custom.cfg yolov4-tiny.weights yolov4-tiny.conv.29 29* Make your custom model yolov4-tiny-obj.cfg based on cfg/yolov4-tiny-custom.cfg instead of yolov4.cfg* Start training: darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolov4-tiny-obj.cfg yolov4-tiny.conv.29
For training Yolo based on other models (DenseNet201-Yolo or ResNet50-Yolo), you can download and get pre-trained weights as showed in this file: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/build/darknet/x64/partial.cmd If you made you custom model that isn't based on other models, then you can train it without pre-trained weights, then will be used random initial weights.
Usually sufficient 2000 iterations for each class(object), but not less than number of training images and not less than 6000 iterations in total. But for a more precise definition when you should stop training, use the following manual:
During training, you will see varying indicators of error, and you should stop when no longer decreases 0.XXXXXXX avg:
Region Avg IOU: 0.798363, Class: 0.893232, Obj: 0.700808, No Obj: 0.004567, Avg Recall: 1.000000, count: 8 Region Avg IOU: 0.800677, Class: 0.892181, Obj: 0.701590, No Obj: 0.004574, Avg Recall: 1.000000, count: 8
9002: 0.211667, 0.60730 avg, 0.001000 rate, 3.868000 seconds, 576128 images Loaded: 0.000000 seconds
9002 - iteration number (number of batch)
0.60730 avg - average loss (error) - the lower, the better
When you see that average loss 0.xxxxxx avg no longer decreases at many iterations then you should stop training. The final avgerage loss can be from 0.05 (for a small model and easy dataset) to 3.0 (for a big model and a difficult dataset).
Or if you train with flag -map then you will see mAP indicator Last accuracy mAP@0.5 = 18.50% in the console - this indicator is better than Loss, so train while mAP increases.
Once training is stopped, you should take some of last .weights-files from darknet\build\darknet\x64\backup and choose the best of them:
For example, you stopped training after 9000 iterations, but the best result can give one of previous weights (7000, 8000, 9000). It can happen due to overfitting. Overfitting - is case when you can detect objects on images from training-dataset, but can't detect objects on any others images. You should get weights from Early Stopping Point:

To get weights from Early Stopping Point:
2.1. At first, in your file obj.data you must specify the path to the validation dataset valid = valid.txt (format of valid.txt as in train.txt), and if you haven't validation images, just copy data\train.txt to data\valid.txt.
2.2 If training is stopped after 9000 iterations, to validate some of previous weights use this commands:
(If you use another GitHub repository, then use darknet.exe detector recall... instead of darknet.exe detector map...)
darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights
darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_8000.weights
darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_9000.weights
And comapre last output lines for each weights (7000, 8000, 9000):
Choose weights-file with the highest mAP (mean average precision) or IoU (intersect over union)
For example, bigger mAP gives weights yolo-obj_8000.weights - then use this weights for detection.
Or just train with -map flag:
darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -map
So you will see mAP-chart (red-line) in the Loss-chart Window. mAP will be calculated for each 4 Epochs using valid=valid.txt file that is specified in obj.data file (1 Epoch = images_in_train_txt / batch iterations)
(to change the max x-axis value - change max_batches= parameter to 2000*classes, f.e. max_batches=6000 for 3 classes)

Example of custom object detection: darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights
IoU (intersect over union) - average instersect over union of objects and detections for a certain threshold = 0.24
mAP (mean average precision) - mean value of average precisions for each class, where average precision is average value of 11 points on PR-curve for each possible threshold (each probability of detection) for the same class (Precision-Recall in terms of PascalVOC, where Precision=TP/(TP+FP) and Recall=TP/(TP+FN) ), page-11: http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/ckiw/postscript/ijcv_voc09.pdf
mAP is default metric of precision in the PascalVOC competition, this is the same as AP50 metric in the MS COCO competition. In terms of Wiki, indicators Precision and Recall have a slightly different meaning than in the PascalVOC competition, but IoU always has the same meaning.

Example of custom object detection: darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights
 |  |
|---|---|
Before training:
set flag random=1 in your .cfg-file - it will increase precision by training Yolo for different resolutions: link
increase network resolution in your .cfg-file (height=608, width=608 or any value multiple of 32) - it will increase precision
check that each object that you want to detect is mandatory labeled in your dataset - no one object in your data set should not be without label. In the most training issues - there are wrong labels in your dataset (got labels by using some conversion script, marked with a third-party tool, ...). Always check your dataset by using: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
my Loss is very high and mAP is very low, is training wrong? Run training with -show_imgs flag at the end of training command, do you see correct bounded boxes of objects (in windows or in files aug_...jpg)? If no - your training dataset is wrong.
for each object which you want to detect - there must be at least 1 similar object in the Training dataset with about the same: shape, side of object, relative size, angle of rotation, tilt, illumination. So desirable that your training dataset include images with objects at diffrent: scales, rotations, lightings, from different sides, on different backgrounds - you should preferably have 2000 different images for each class or more, and you should train 2000*classes iterations or more
desirable that your training dataset include images with non-labeled objects that you do not want to detect - negative samples without bounded box (empty .txt files) - use as many images of negative samples as there are images with objects
What is the best way to mark objects: label only the visible part of the object, or label the visible and overlapped part of the object, or label a little more than the entire object (with a little gap)? Mark as you like - how would you like it to be detected.
for training with a large number of objects in each image, add the parameter max=200 or higher value in the last [yolo]-layer or [region]-layer in your cfg-file (the global maximum number of objects that can be detected by YoloV3 is 0,0615234375*(width*height) where are width and height are parameters from [net] section in cfg-file)
for training for small objects (smaller than 16x16 after the image is resized to 416x416) - set layers = 23 instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L895
set stride=4 instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L892
set stride=4 instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L989
for training for both small and large objects use modified models:
Full-model: 5 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov3_5l.cfg
Tiny-model: 3 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov4-tiny_3l.cfg
YOLOv4: 3 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov4-custom.cfg
If you train the model to distinguish Left and Right objects as separate classes (left/right hand, left/right-turn on road signs, ...) then for disabling flip data augmentation - add flip=0 here: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/3d2d0a7c98dbc8923d9ff705b81ff4f7940ea6ff/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L17
General rule - your training dataset should include such a set of relative sizes of objects that you want to detect:
train_network_width * train_obj_width / train_image_width ~= detection_network_width * detection_obj_width / detection_image_width
train_network_height * train_obj_height / train_image_height ~= detection_network_height * detection_obj_height / detection_image_height
I.e. for each object from Test dataset there must be at least 1 object in the Training dataset with the same class_id and about the same relative size:
object width in percent from Training dataset ~= object width in percent from Test dataset
That is, if only objects that occupied 80-90% of the image were present in the training set, then the trained network will not be able to detect objects that occupy 1-10% of the image.
to speedup training (with decreasing detection accuracy) set param stopbackward=1 for layer-136 in cfg-file
each: model of object, side, illimination, scale, each 30 grad of the turn and inclination angles - these are different objects from an internal perspective of the neural network. So the more different objects you want to detect, the more complex network model should be used.
to make the detected bounded boxes more accurate, you can add 3 parameters ignore_thresh = .9 iou_normalizer=0.5 iou_loss=giou to each [yolo] layer and train, it will increase mAP@0.9, but decrease mAP@0.5.
Only if you are an expert in neural detection networks - recalculate anchors for your dataset for width and height from cfg-file:darknet.exe detector calc_anchors data/obj.data -num_of_clusters 9 -width 416 -height 416then set the same 9 anchors in each of 3 [yolo]-layers in your cfg-file. But you should change indexes of anchors masks= for each [yolo]-layer, so for YOLOv4 the 1st-[yolo]-layer has anchors smaller than 30x30, 2nd smaller than 60x60, 3rd remaining, and vice versa for YOLOv3. Also you should change the filters=(classes + 5)*<number of mask> before each [yolo]-layer. If many of the calculated anchors do not fit under the appropriate layers - then just try using all the default anchors.
After training - for detection:
Increase network-resolution by set in your .cfg-file (height=608 and width=608) or (height=832 and width=832) or (any value multiple of 32) - this increases the precision and makes it possible to detect small objects: link
it is not necessary to train the network again, just use .weights-file already trained for 416x416 resolution
to get even greater accuracy you should train with higher resolution 608x608 or 832x832, note: if error Out of memory occurs then in .cfg-file you should increase subdivisions=16, 32 or 64: link
Here you can find repository with GUI-software for marking bounded boxes of objects and generating annotation files for Yolo v2 - v4: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
With example of: train.txt, obj.names, obj.data, yolo-obj.cfg, air1-6.txt, bird1-4.txt for 2 classes of objects (air, bird) and train_obj.cmd with example how to train this image-set with Yolo v2 - v4
Different tools for marking objects in images:
in C++: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
in Python: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
in Python: https://github.com/Cartucho/OpenLabeling
in C++: https://www.ccoderun.ca/darkmark/
in JavaScript: https://github.com/opencv/cvat
in C++: https://github.com/jveitchmichaelis/deeplabel
in C#: https://github.com/BMW-InnovationLab/BMW-Labeltool-Lite
DL-Annotator for Windows ($30): url
v7labs - the greatest cloud labeling tool ($1.5 per hour): https://www.v7labs.com/
on Linux
using build.sh or
build darknet using cmake or
set LIBSO=1 in the Makefile and do make
on Windows
using build.ps1 or
build darknet using cmake or
compile build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll.sln solution or build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll_no_gpu.sln solution
There are 2 APIs:
C API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/include/darknet.h
Python examples using the C API:
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/darknet.py
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/darknet_video.py
C++ API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/include/yolo_v2_class.hpp
C++ example that uses C++ API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp
To compile Yolo as C++ DLL-file yolo_cpp_dll.dll - open the solution build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll.sln, set x64 and Release, and do the: Build -> Build yolo_cpp_dll
You should have installed CUDA 10.0
To use cuDNN do: (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> Preprocessor -> Preprocessor Definitions, and add at the beginning of line: CUDNN;
To use Yolo as DLL-file in your C++ console application - open the solution build\darknet\yolo_console_dll.sln, set x64 and Release, and do the: Build -> Build yolo_console_dll
you can run your console application from Windows Explorer build\darknet\x64\yolo_console_dll.exeuse this command: yolo_console_dll.exe data/coco.names yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4
after launching your console application and entering the image file name - you will see info for each object:
<obj_id> <left_x> <top_y> <width> <height> <probability>
to use simple OpenCV-GUI you should uncomment line //#define OPENCV in yolo_console_dll.cpp-file: link
you can see source code of simple example for detection on the video file: link
yolo_cpp_dll.dll-API: link
struct bbox_t {
unsigned int x, y, w, h; // (x,y) - top-left corner, (w, h) - width & height of bounded box
float prob; // confidence - probability that the object was found correctly
unsigned int obj_id; // class of object - from range [0, classes-1]
unsigned int track_id; // tracking id for video (0 - untracked, 1 - inf - tracked object)
unsigned int frames_counter;// counter of frames on which the object was detected
};
class Detector {
public:
Detector(std::string cfg_filename, std::string weight_filename, int gpu_id = 0);
~Detector();
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(std::string image_filename, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(image_t img, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
static image_t load_image(std::string image_filename);
static void free_image(image_t m);
#ifdef OPENCV
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(cv::Mat mat, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
std::shared_ptr<image_t> mat_to_image_resize(cv::Mat mat) const;
#endif
}; 代码语言分布